What is Bitcoin and How Does It Work kicks off the ultimate guide to understanding the digital currency revolution, taking you on a journey through the world of cryptocurrency with a fresh perspective.
Dive deep into the inner workings of Bitcoin as we unravel its mysteries and explore its impact on the global economy.
What is Bitcoin?: What Is Bitcoin And How Does It Work
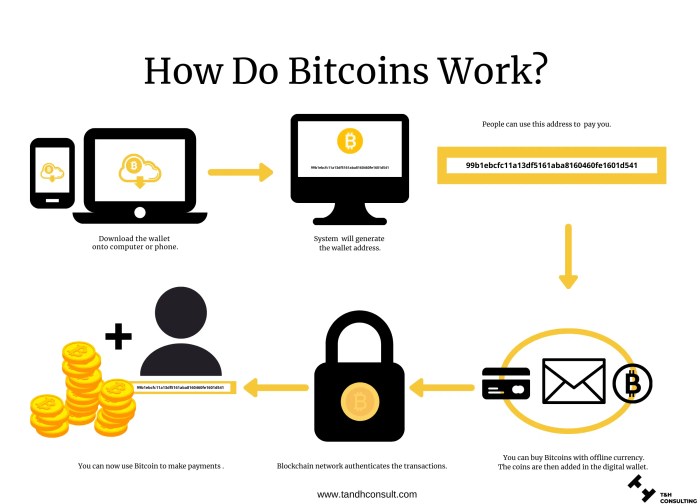
Bitcoin is a digital currency that operates on a decentralized network, allowing peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central authority like a bank or government. This virtual currency can be used for online purchases, investments, or as a store of value.
Decentralized Nature of Bitcoin
- Bitcoin is decentralized, meaning it is not controlled by any single entity or government.
- Transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded on a public ledger called the blockchain.
- This decentralized system ensures greater security, transparency, and independence from traditional financial institutions.
Role of Blockchain Technology
- The blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores all Bitcoin transactions across a network of computers.
- Each block contains a list of transactions, and once verified, it is added to the chain in a chronological order.
- Blockchain technology ensures the integrity and security of transactions, making it virtually impossible to alter past records.
Comparison to Traditional Fiat Currencies
- Bitcoin is not issued or regulated by any government, unlike traditional fiat currencies such as the US Dollar or Euro.
- Unlike fiat currencies, Bitcoin has a limited supply, with only 21 million coins that can ever be mined.
- Bitcoin transactions are pseudonymous, providing a level of privacy and security not always present in traditional banking systems.
How does Bitcoin work?
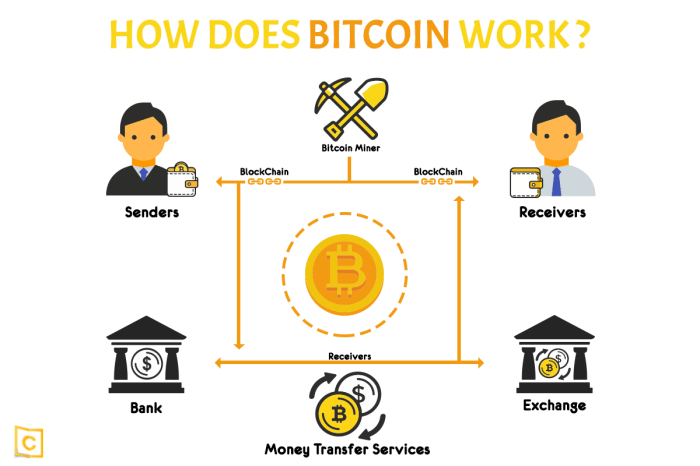
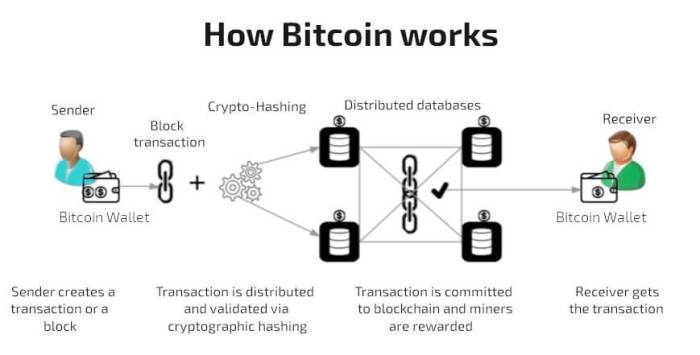
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network called blockchain, where transactions are recorded in a public ledger without the need for a central authority like a bank.
The process of mining Bitcoin, What is Bitcoin and How Does It Work
- Miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems that validate transactions.
- Once a miner solves the problem, a new block is added to the blockchain, and the miner is rewarded with newly minted Bitcoins.
- This process ensures the security and integrity of the network.
Explain how transactions are verified and added to the blockchain
- When a transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to the network for validation.
- Miners verify the transaction by including it in a block along with other transactions.
- Once verified, the block is added to the blockchain, making the transaction irreversible.
Discuss the role of private and public keys in Bitcoin transactions
- Public keys are used to receive Bitcoin, similar to an account number.
- Private keys are used to access and authorize the transfer of Bitcoin from one wallet to another.
- Both keys work together to ensure the security and privacy of transactions.
Describe the security features of the Bitcoin network
- The decentralized nature of the blockchain makes it resistant to hacking and fraud.
- Transactions are encrypted and verified by multiple nodes in the network, making it highly secure.
- Each transaction is linked to the previous one, creating a chain that is difficult to alter, ensuring the integrity of the system.
What is the history of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin was created in 2008 by an unknown person or group of people using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It was released as open-source software in 2009, marking the beginning of the era of cryptocurrencies.
Creation of Bitcoin
- The concept of Bitcoin was Artikeld in a whitepaper titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” published by Satoshi Nakamoto in October 2008.
- The first Bitcoin software and the first block of the Bitcoin blockchain, known as the Genesis Block, were mined by Nakamoto in January 2009.
Major Milestones
- In May 2010, the first real-world transaction using Bitcoin occurred when Laszlo Hanyecz purchased two pizzas for 10,000 BTC, establishing the value of Bitcoin for the first time.
- In 2013, Bitcoin’s value surpassed $1,000 for the first time, attracting mainstream attention and increasing adoption.
- In 2017, Bitcoin’s price surged to nearly $20,000, leading to a frenzy of investment and media coverage.
First Bitcoin Transaction
The first Bitcoin transaction involved the purchase of two pizzas for 10,000 BTC, highlighting the potential real-world applications of the cryptocurrency.
Regulatory Challenges
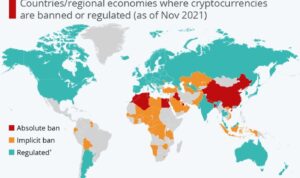
- Bitcoin has faced regulatory challenges globally due to concerns about its potential use in illegal activities, volatility, and lack of centralized control.
- Various countries have imposed restrictions or outright bans on Bitcoin trading and mining, while others have embraced it through regulatory frameworks.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Bitcoin?
Bitcoin offers several advantages as a digital currency, but it also comes with certain risks and drawbacks. Let’s explore the benefits and downsides of using Bitcoin.
Advantages of Using Bitcoin
- Decentralization: Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network, meaning it is not controlled by any government or financial institution.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Bitcoin transactions typically have lower fees compared to traditional banking systems.
- Global Accessibility: Bitcoin can be used for transactions across borders without the need for currency conversion.
- Security and Anonymity: Transactions made with Bitcoin are secure and offer a certain level of anonymity.
- Transparency: The blockchain technology behind Bitcoin allows for transparent and traceable transactions.
Disadvantages of Using Bitcoin
- Volatility: The value of Bitcoin can be highly volatile, leading to potential financial losses.
- Lack of Regulation: Bitcoin is not regulated by any central authority, which can make it susceptible to fraud and illegal activities.
- Irreversible Transactions: Once a Bitcoin transaction is confirmed, it cannot be reversed, which can be a disadvantage in case of errors or fraud.
- Technical Complexity: Using Bitcoin requires a certain level of technical knowledge and understanding of digital wallets and security measures.
- Environmental Impact: The process of mining Bitcoin consumes a significant amount of energy, raising concerns about its environmental impact.
Comparison of Bitcoin Transactions with Traditional Banking Systems
Bitcoin transactions are typically faster and more cost-effective compared to traditional banking systems. While traditional bank transfers can take several days to process, Bitcoin transactions are usually completed within minutes. Additionally, the fees associated with Bitcoin transactions are often lower than those charged by banks for international transfers.
Impact of Bitcoin on the Global Economy
Bitcoin has the potential to disrupt traditional financial systems and reshape the global economy. Its decentralization and transparency could lead to greater financial inclusivity and efficiency. However, its volatility and regulatory challenges may also pose risks to the stability of the global economy.