Retirement Planning Guide takes center stage as we dive into the world of securing your financial future with style and confidence. Get ready to explore the ins and outs of retirement planning in a way that’s informative and fun!
Importance of Retirement Planning: Retirement Planning Guide
Planning for retirement is crucial for ensuring financial security in the later years of life. By setting aside funds and investments early on, individuals can build a nest egg that will support them through retirement. Without a solid plan in place, retirees may struggle to cover expenses and maintain their desired lifestyle.
Impact of Early Retirement Planning, Retirement Planning Guide
Early retirement planning can have a significant impact on financial stability. By starting to save and invest at a young age, individuals can take advantage of compound interest and grow their retirement funds over time. This can lead to a more comfortable retirement with fewer financial worries.
Mitigating Unforeseen Circumstances
Retirement planning can also help mitigate unforeseen circumstances that may arise later in life. For example, unexpected medical expenses, changes in the economy, or the need for long-term care can all put a strain on finances. By having a well-thought-out retirement plan, individuals can better prepare for these challenges and ensure they are financially protected.
Types of Retirement Accounts
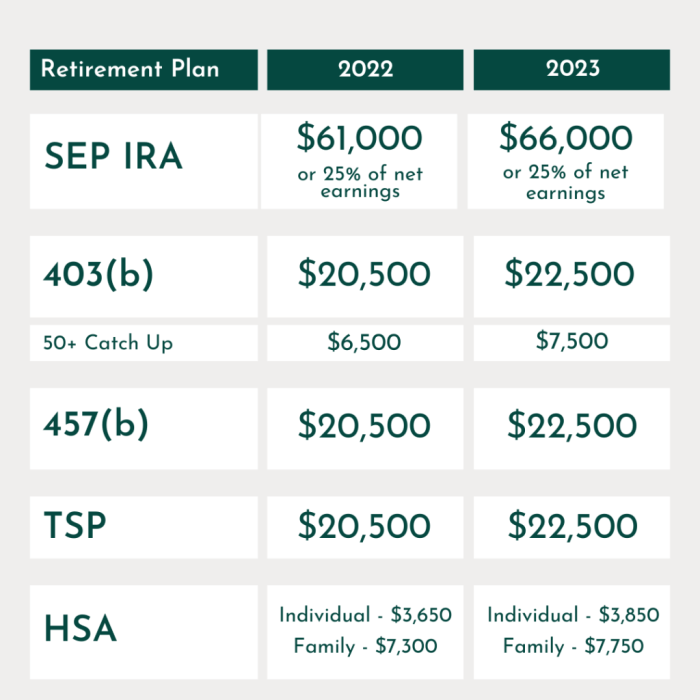
When planning for retirement, it’s essential to understand the different types of retirement accounts available to help you save for your future. Each type of account comes with its own set of benefits and limitations, as well as unique tax implications. Let’s take a closer look at some common retirement accounts:
401(k)
A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement account that allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income to save for retirement. One of the key benefits of a 401(k) is that contributions are often matched by employers, providing an instant boost to your savings. However, there are limitations on when and how you can access the funds, as well as restrictions on investment options.
IRA (Individual Retirement Account)
An IRA is a retirement account that individuals can open on their own, outside of an employer-sponsored plan. There are different types of IRAs, including traditional IRAs and Roth IRAs. Traditional IRAs allow for tax-deferred growth, meaning you won’t pay taxes on your contributions until you withdraw the funds in retirement. Roth IRAs, on the other hand, are funded with after-tax dollars, but withdrawals in retirement are tax-free.
Pension Plans
Pension plans are retirement accounts typically offered by employers that provide a fixed monthly payment to retirees based on factors such as salary and years of service. One of the main advantages of a pension plan is the guaranteed income it offers during retirement. However, not all employers offer pension plans, and they may come with restrictions on how and when you can access the funds.
Tax Implications
When it comes to tax implications, traditional retirement accounts like 401(k)s and traditional IRAs offer tax-deferred growth, meaning you won’t pay taxes on your contributions until you withdraw the funds in retirement. On the other hand, Roth retirement accounts like Roth IRAs are funded with after-tax dollars, so withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. Understanding the tax implications of each type of retirement account can help you make informed decisions about where to save for retirement.
Setting Retirement Goals

Setting retirement goals is a crucial step in ensuring financial security and peace of mind during your golden years. It involves determining how much money you will need to live comfortably and sustain your desired lifestyle after you stop working.When setting retirement goals, consider the following tips to make them realistic and achievable based on your individual needs and circumstances:
Factors to Consider for Retirement Goals
- Calculate your current expenses: Start by assessing your current expenses to estimate how much you will need to cover your basic living costs in retirement.
- Consider inflation: Account for inflation when projecting your future expenses to ensure that your retirement savings will be sufficient to maintain your purchasing power.
- Think about healthcare costs: Healthcare expenses tend to increase as you age, so factor in potential medical costs when setting your retirement goals.
Determining Retirement Age and Desired Income
- Retirement age: Decide at what age you would like to retire and consider how many years of retirement you need to plan for.
- Desired income: Determine the annual income you will need in retirement to support your lifestyle and cover all expenses, including discretionary spending.
- Social Security and other income sources: Take into account any other sources of income, such as Social Security benefits or pensions, when calculating your desired retirement income.
Adjusting Retirement Goals Over Time
- Monitor your progress: Regularly review your retirement savings and investment accounts to track your progress towards meeting your goals.
- Life changes: Be prepared to adjust your retirement goals as your life circumstances change, such as unexpected expenses, health issues, or changes in income.
- Seek professional advice: Consider consulting with a financial advisor to help you assess your retirement goals and make any necessary adjustments to ensure financial security in retirement.
Investment Strategies for Retirement
When it comes to planning for retirement, choosing the right investment strategies is crucial to ensure financial security in your golden years. Let’s explore various investment options and tips to help you make informed decisions.
Stocks
- Stocks represent ownership in a company and can offer high potential returns.
- However, they also come with higher risk due to market volatility.
- Diversifying your stock portfolio is essential to reduce risk.
Bonds
- Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations.
- They provide a fixed income stream and are generally considered less risky than stocks.
- Including bonds in your portfolio can provide stability and income.
Mutual Funds
- Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities.
- They offer instant diversification and professional management.
- Choose mutual funds that align with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Real Estate
- Investing in real estate can provide rental income and potential property appreciation.
- It offers a tangible asset that can serve as a hedge against inflation.
- Consider factors like location, property type, and market trends before investing in real estate.
Asset Allocation and Diversification
Asset allocation involves dividing your investments among different asset classes like stocks, bonds, and cash to manage risk.
Diversification is spreading your investments within each asset class to further reduce risk.
- By diversifying your portfolio, you can minimize the impact of market fluctuations on your overall investment.
- Regularly review and rebalance your portfolio to maintain your desired asset allocation.
Managing Investment Risk
- Consider your risk tolerance and investment timeline when choosing investments.
- Understand the risks associated with each investment option and seek professional advice if needed.
- Monitor your investments regularly and make adjustments as necessary to stay on track with your retirement goals.
Healthcare and Insurance in Retirement
When it comes to retirement planning, healthcare and insurance play a crucial role in ensuring financial stability and peace of mind during your golden years. Let’s dive into the importance of healthcare and insurance coverage during retirement.
Medicare Coverage
Medicare is a federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It consists of different parts that cover hospital stays, doctor visits, prescription drugs, and more. It’s essential to understand the different parts of Medicare and how they work together to provide comprehensive coverage for your healthcare needs.
Supplemental Insurance Options
While Medicare provides basic health coverage, it may not cover all of your healthcare expenses. Supplemental insurance, such as Medigap policies or Medicare Advantage plans, can help fill the gaps in coverage and reduce out-of-pocket costs. These plans offer additional benefits and services that can enhance your overall healthcare experience in retirement.
Long-Term Care Considerations
Long-term care, including services like nursing home care or home health aides, can be a significant expense during retirement. Planning for long-term care needs in advance can help protect your savings and ensure you receive the care you need as you age. Long-term care insurance is an option to consider to help cover these costs and provide financial security for you and your loved ones.
Estimating and Planning for Healthcare Expenses
Estimating healthcare expenses in retirement can be challenging, as costs can vary based on individual health needs and circumstances. It’s important to create a realistic budget that accounts for premiums, deductibles, copayments, and other out-of-pocket expenses. Consider factors like inflation and potential health issues as you project your healthcare costs in retirement. Consulting with a financial advisor or healthcare expert can help you develop a comprehensive plan to cover your healthcare needs throughout your retirement years.





